Your credit score is a crucial factor in determining your financial health. It influences loan approvals, interest rates, and even potential employment opportunities. Understanding how credit scores are calculated can empower you to make informed decisions and improve your financial standing.
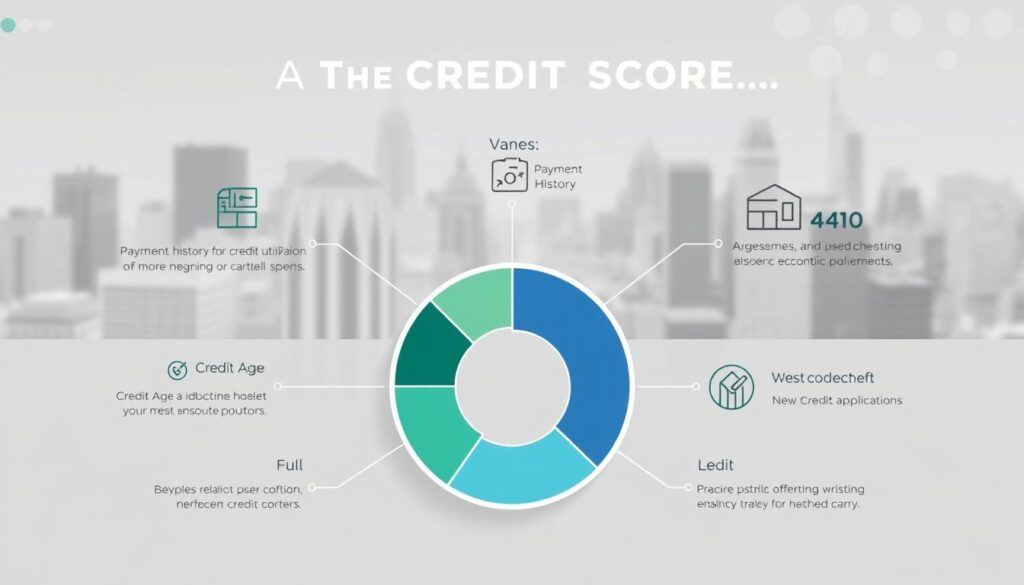
Payment history, credit utilization, and the number of accounts are key factors in determining your credit score. Scoring models, such as those from FICO and VantageScore, use these elements to generate your score. Even minor differences in these factors can lead to significant variations in the scores provided by different lenders.

Multiple credit bureaus may report different scores due to varied data sources and reporting practices. The calculation process involves evaluating debt, account history, and credit utilization ratios. Understanding these aspects is essential for managing your financial portfolio effectively.
Understanding Credit Scores and Their Importance
Your credit score is a three-digit number that reflects your financial reliability. It plays a key role in decisions made by lenders, landlords, and even some employers. A good score can open doors to better loan terms and lower interest rates.

What Exactly Is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a numerical measure of your creditworthiness, typically ranging from 300 to 850. It’s calculated based on factors like payment history, credit utilization, and the types of credit you use. Different scoring models, such as FICO and VantageScore, may give you slightly different scores.
Why Your Credit Score Matters in the United States
In the U.S., your credit score is crucial for securing loans, mortgages, and credit cards. It influences the interest rates you’ll pay and can even affect your ability to rent an apartment or get a job. Maintaining a healthy mix of credit types and keeping your utilization ratio low can significantly boost your score.
Demystifying Credit Scores: How They’re Calculated
Understanding how your credit score is determined can help you manage your finances better. Your score is influenced by several key factors, each carrying different weights. Let’s break down these components and their impact.
Payment History: The Foundation of Your Score
Payment history is the most significant factor, making up 35% of your score. Late payments, defaults, or accounts sent to collections can significantly lower your score. On-time payments, however, help build a positive credit history.
Credit Utilization: Keeping the Balance
Credit utilization, accounting for 30% of your score, is the ratio of used credit to your available credit limit. Keeping this ratio below 30% is ideal. For example, if your credit limit is $1,000, try to keep your balance under $300.
Scoring Models: FICO vs. VantageScore
Two main models dominate credit scoring: FICO and VantageScore. While both consider similar factors, the weights differ. FICO places more emphasis on payment history and credit utilization, whereas VantageScore focuses on debt-to-credit ratio and credit history length.
| Factor | FICO Weight | VantageScore Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Payment History | 35% | 41% |
| Credit Utilization | 30% | 20% |
| Credit History Length | 15% | 20% |
| Credit Mix | 10% | 11% |
| New Credit | 10% | 8% |
New Credit and Hard Inquiries
New credit inquiries can temporarily lower your score. Hard inquiries, which occur when lenders check your credit for loan or credit card applications, can reduce your score by a few points. Soft inquiries, like checking your own credit, don’t affect your score.
Understanding these factors empowers you to make informed decisions. By maintaining a healthy mix of credit types, keeping utilization low, and avoiding excessive new credit applications, you can work towards a stronger financial profile.
Strategies to Improve and Manage Your Credit Score
Enhancing your credit score requires a combination of smart financial decisions and consistent habits. By focusing on key areas, you can build a stronger financial foundation and enjoy better loan terms.
Tips for Reducing Credit Utilization Effectively
One of the most impactful ways to boost your score is by lowering your credit utilization. This is the ratio of your used credit to your available credit limit. Aim to keep this below 30% for all your accounts. For instance, if your limit is $1,000, try to keep your balance under $300. Paying down revolving credit balances and responsibly increasing your credit limits can help reduce this ratio.
Remember, even small reductions in utilization can lead to noticeable score improvements. Consistency is key to building a positive track record.
Building and Maintaining a Strong Payment History
Payment history is the most significant factor in your credit score, making up 35% of the total. Late payments can harm your score, so setting up reminders or automating your payments can help maintain a spotless record. On-time payments demonstrate financial responsibility and are crucial for a healthy score.
Monitoring Your Credit Report for Accuracy
Regularly reviewing your credit report is essential for catching errors. Inaccuracies can lower your score, so it’s important to dispute any mistakes immediately. You can request free reports from the three major bureaus annually. Ensuring your report is accurate helps lenders see your true financial situation.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage your credit and work towards a higher score. Remember, consistent habits and practical management are vital for long-term financial success.
Conclusion
Understanding how your credit score is determined and maintaining good credit habits can significantly impact your financial health. Your score serves as a key indicator of your financial reliability, influencing loan approvals, interest rates, and even employment opportunities.
Key factors such as payment history, credit utilization, and the length of your credit history play a crucial role in determining your score. Monitoring your credit report for accuracy and avoiding hard inquiries are essential steps in maintaining a healthy financial profile.
By implementing practical strategies like reducing credit utilization and making timely payments, you can steadily improve your score. Remember, even small enhancements can lead to more favorable loan terms and increased financial opportunities.
Take control of your financial future by reviewing your credit report today. Every improvement, no matter how minor, brings you closer to achieving better financial outcomes. Start your journey toward a stronger financial profile now.
FAQ
How does payment history impact my credit score?
Your payment history is a key factor in determining your credit score. It accounts for about 35% of your total score. On-time payments boost your score, while late payments or accounts sent to collections can lower it. Consistency in paying bills shows lenders you manage debt responsibly.
What role does credit utilization play in scoring?
Credit utilization ratio is the percentage of your available credit being used. It makes up about 30% of your score. Keeping this ratio below 30% is recommended, as high utilization can signal financial strain. Aim for lower balances to improve your score over time.
How does the length of credit history affect scoring?
Your credit history length influences about 15% of your score. A longer history, with older accounts, can positively impact your score. It shows lenders you have experience managing credit over time. Avoid closing old accounts to maintain a strong history.
Can applying for new credit hurt my score?
Yes, applying for new credit can temporarily lower your score. Hard inquiries, which occur when lenders check your credit, can reduce your score by a few points. Limit applications and only apply for credit when necessary to minimize the impact.
How does a mix of credit types affect scoring?
A diverse mix of credit, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can improve your score. It shows you can manage different types of debt responsibly. However, it’s not necessary to take on unnecessary debt to achieve this mix.
How often is my credit score updated?
Your credit score is updated regularly, often monthly or quarterly, as new information is added to your credit report. Changes in payment history, balances, or new accounts can trigger updates to your score.
Can I improve my score by paying off debt?
Yes, paying off debt can help improve your score. Reducing credit card balances lowers your credit utilization ratio, which positively impacts your score. Focus on high-interest debt first to maximize the benefit.
How long does it take to rebuild a damaged credit score?
Rebuilding a damaged credit score takes time and effort. Positive changes, like on-time payments and reduced debt, can start to improve your score within a few months. However, significant improvements may take 1-2 years or more.
Does checking my credit report hurt my score?
Checking your own credit report is a soft inquiry and does not lower your score. Monitoring your report regularly is a good practice to ensure accuracy and detect potential fraud.
How does a mortgage affect my credit score?
A mortgage is considered a positive credit mix and can help improve your score if payments are made on time. However, missing payments can significantly lower your score. Consistency is key to maintaining a strong score.
Can I have a good score with only one credit account?
Yes, but it may be more challenging. Having only one account limits your credit mix, which makes up 10% of your score. Adding a diversified mix of accounts over time can strengthen your credit profile.










